Congratulations to Ph.D. student Tiancheng Sheng & Lingyi Zheng et.al. published an article in Cell “Device“
In the article, “Modular brain-machine interface for neurorecording, neurostimulation, and drug delivery“,Sheng et al present a modular multimodal brain-machine interface (BMI) device capable of adapting different configurations, modalities, and capabilities. The modular device can be configured to support neurorecording, neurostimulation, and drug delivery, and its unified interfaces facilitates plug-andplay usage. The applicability of the BMI was demonstrated across four scenarios, including closed-loop seizure modulation in free-moving rats, cortical and depth recording in swine, alpha wave detection in humans, and directional neurostimulation in vitro.
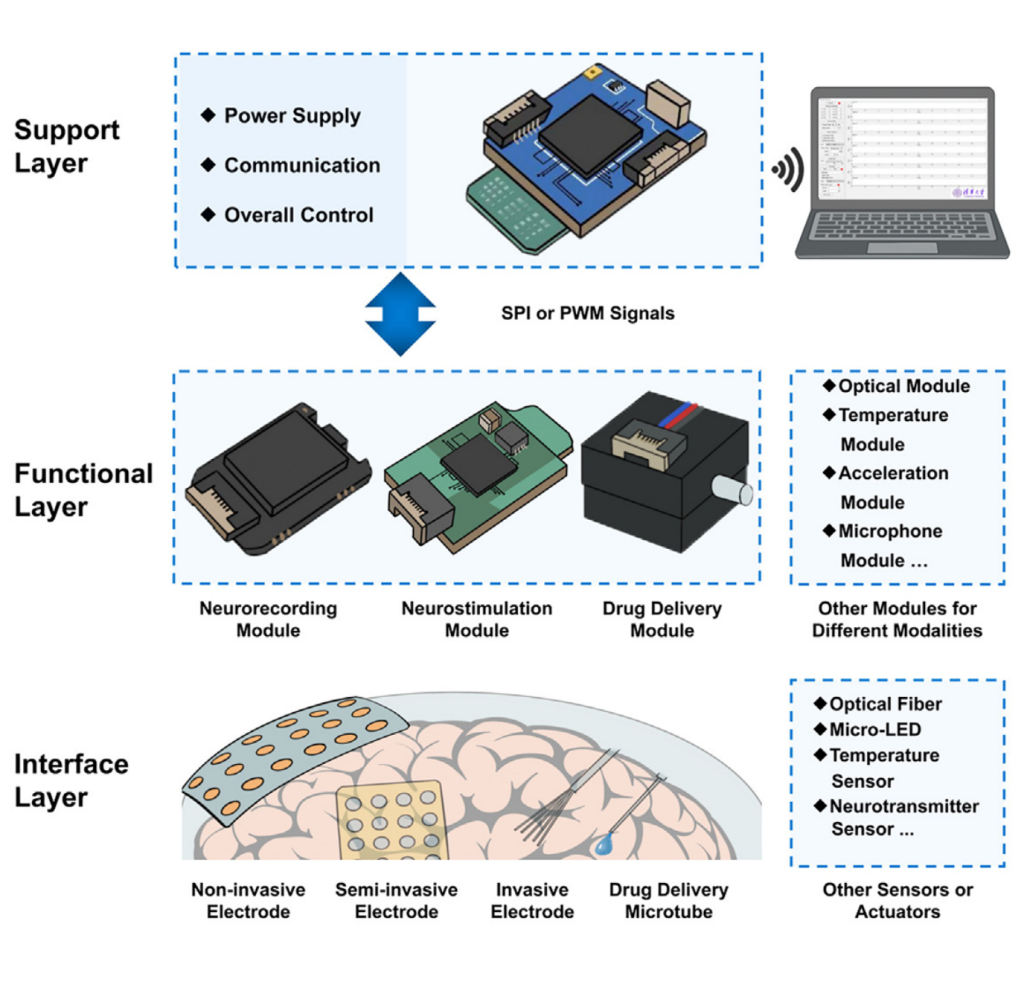
Fig. 1 Graphical abstract of the Modular brain-machine interface
Highlights
- A modular multimodal BMI adapting its configurations to various application scenarios
- A BMI supporting neurorecording, neurostimulation, and drug delivery
- Unified interfaces between modules facilitating plug-andplay reconfiguration
THE BIGGER PICTURE
Brain-machine interface (BMI) devices enable the electric charge, material, and information interactions between the brain and the outside world, facilitating neural decoding, neurological disease diagnosis and treatment, and brain science research. With the advancement of neuroscience, multimodal BMIs, which enable neurorecording, neurostimulation, and drug delivery, have drawn increasingly broad attention from researchers, clinical scientists, and physicians. However, most existing multimodal BMI devices were designed for specific scenarios with highly integrated and fixed configurations. Here, we present a plug-and-play modular multimodal BMI that can adapt configurations, modalities, and capabilities to different experimental requirements. This modular device provides a platform for applications that require multiple modalities and device specifications.
For more information, please visit the article directly. Link to original article:
Sheng et al., Modular brain-machine interface for neurorecording, neurostimulation, and drug delivery, Device
(2025), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.device.2024.100687
